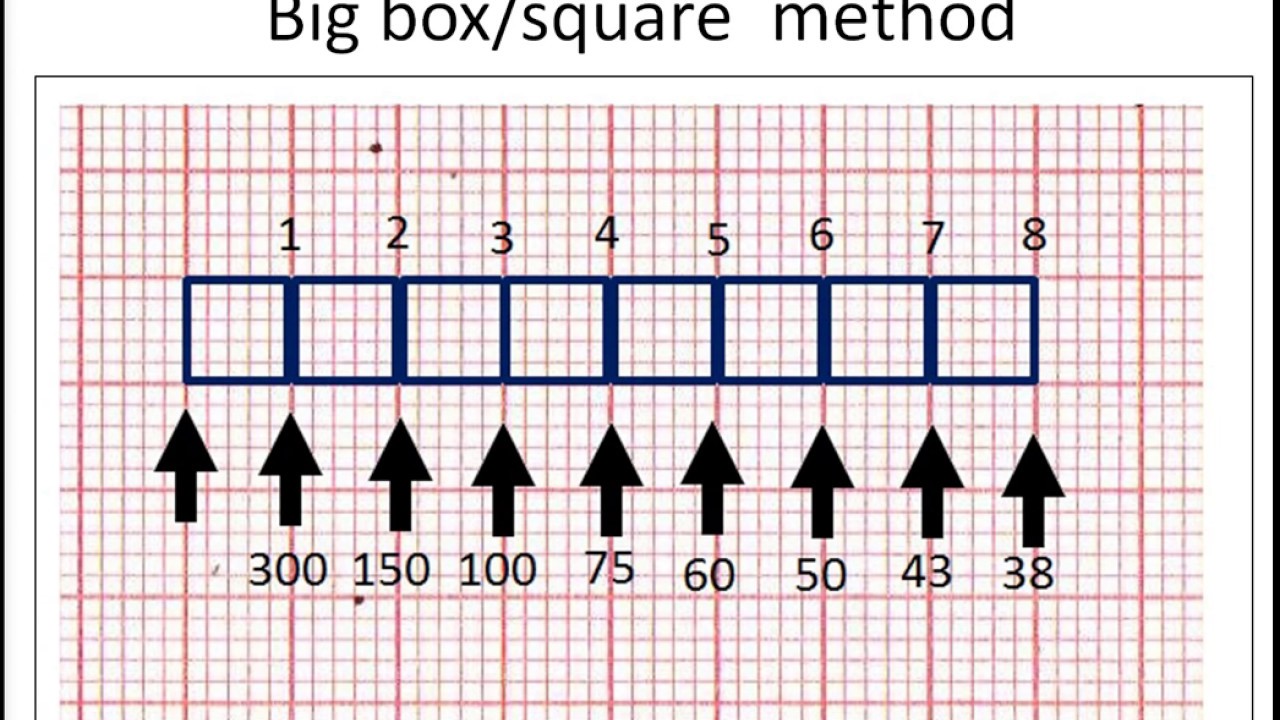
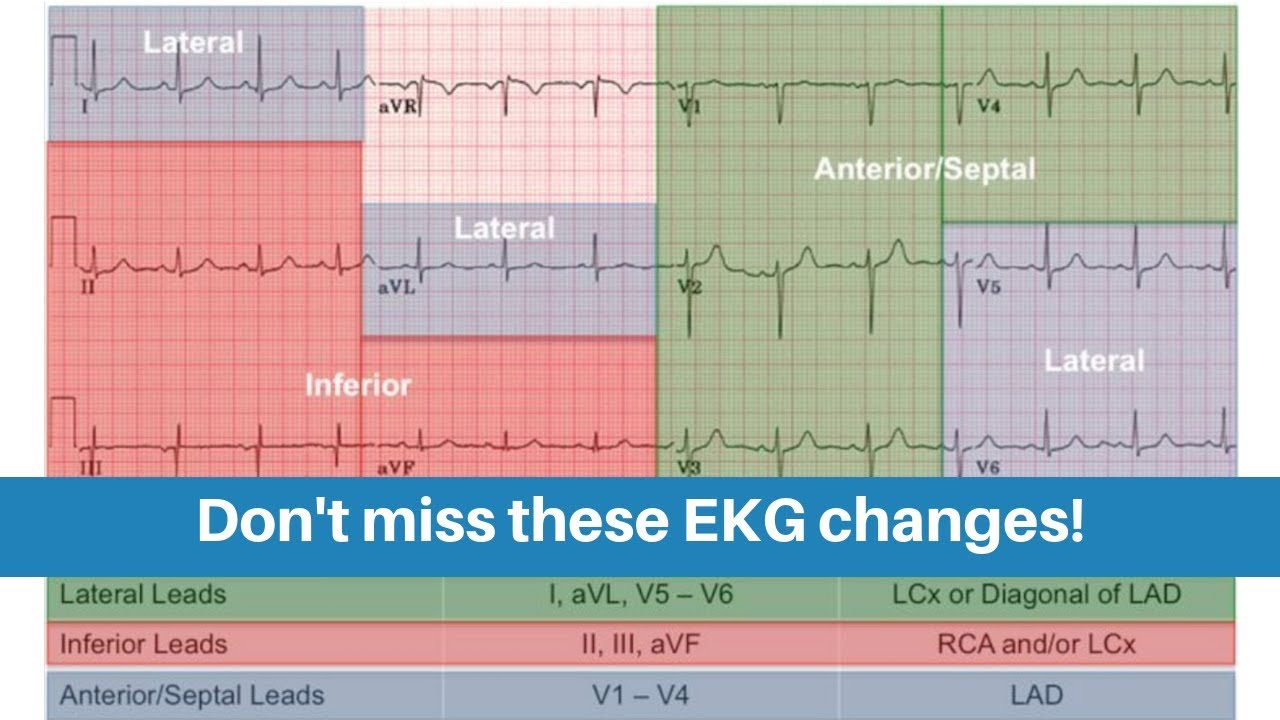
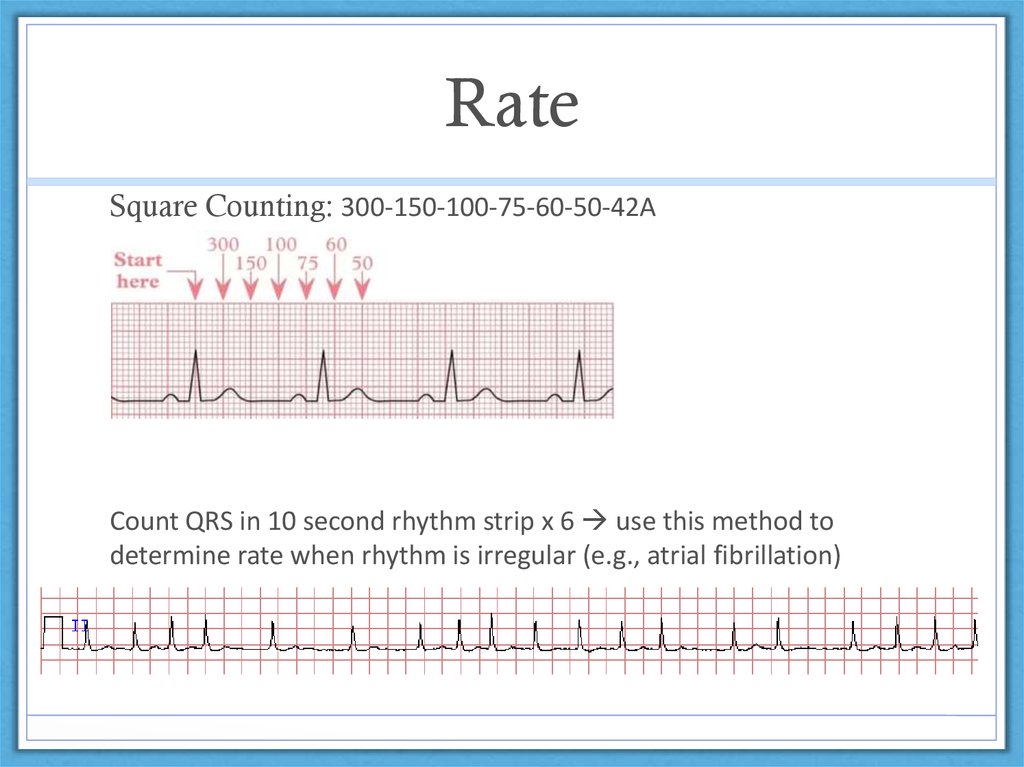
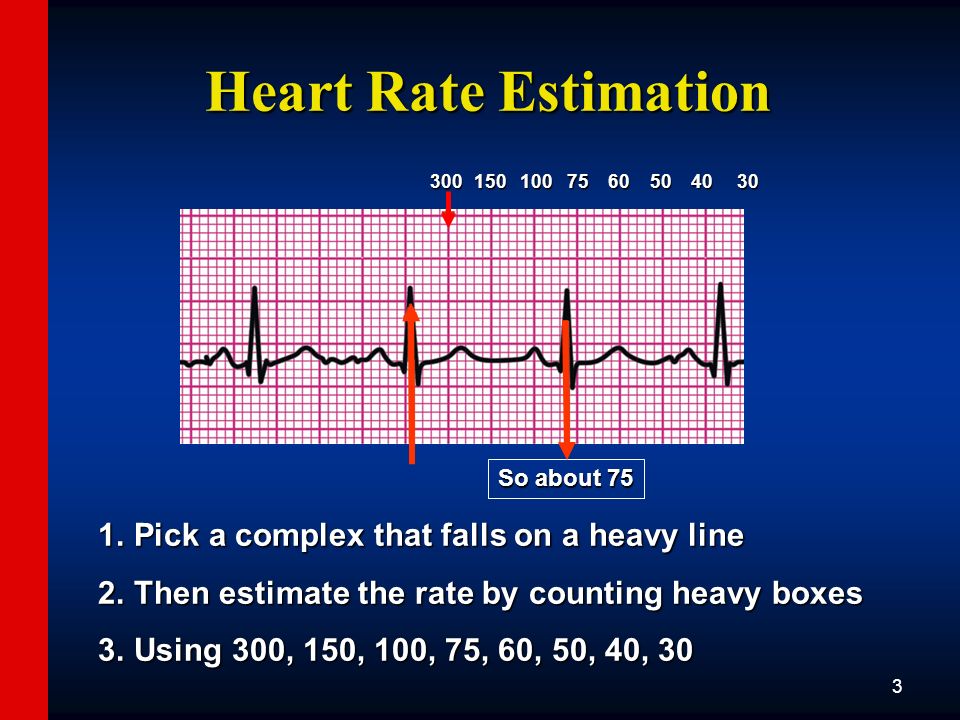
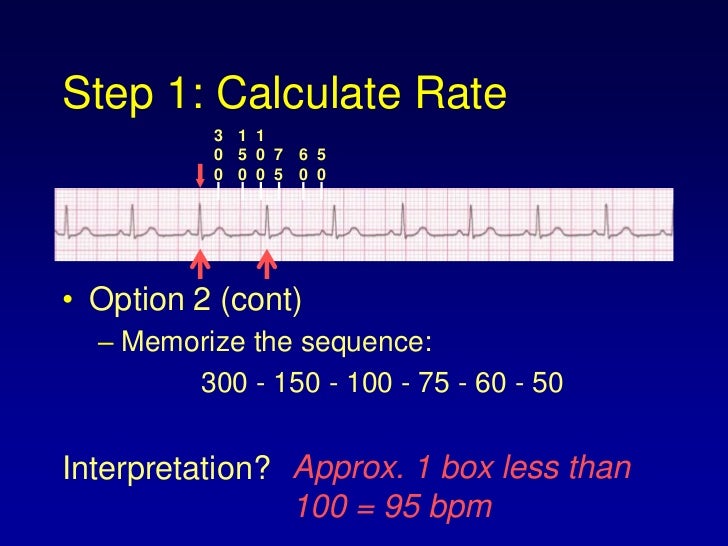
The mnemonic "" to estimate the rate in beats per minute (BPM) In other words if you pass 2 lines before the next QRS, the heart rate (HR) would be less than 150 Remember that this is merely an estimate You should useExample #3 These QRS complexes are less than two large boxes apart, thus the heart rate is between 150 and 300 bpm Multiply the number of QRS complexes byLead I should be opposite of AVR (in a normal EKG) Rwave should progress in chest leads (V leads) such that by V4 Memorize 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 37
Www Canadianveterinarians Net Documents Dr Meg Sleeper The Abcs Of Ecgs Back To Basics Part I
What is the 300 rule for ecg
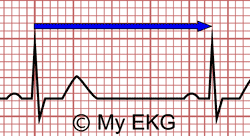
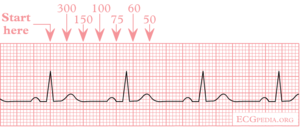
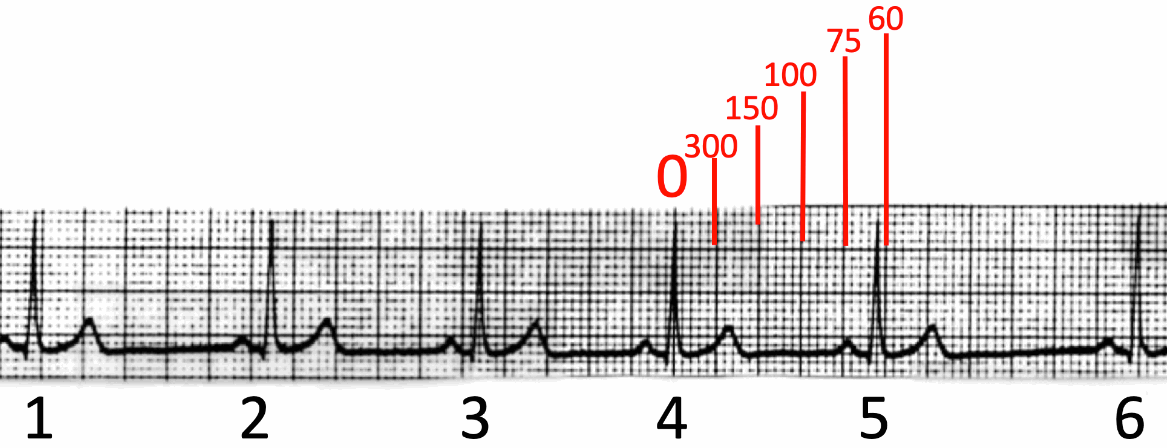
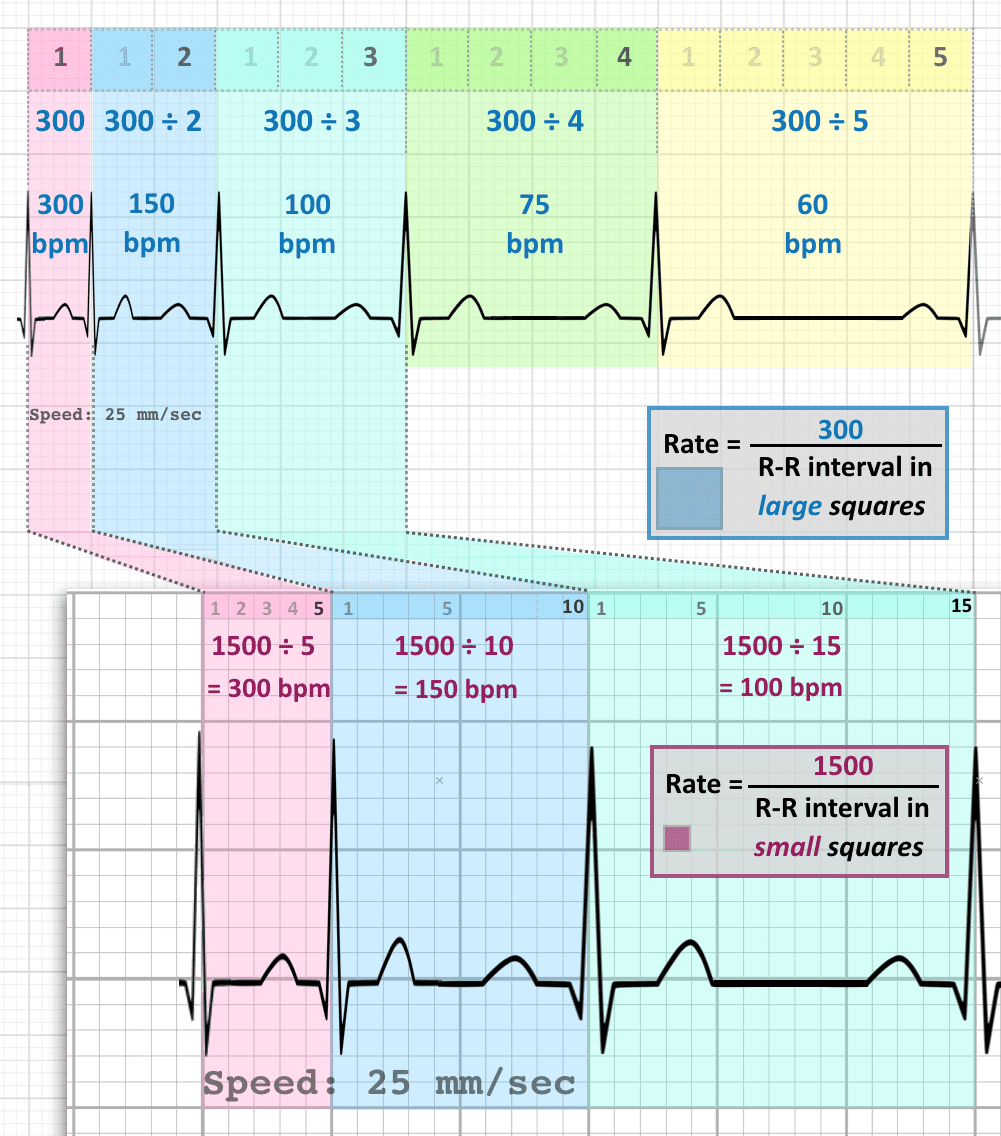
What is the 300 rule for ecg- Use the sequence Count from the first QRS complex, the first thick line is 300, the next thick line 150 etc Stop the sequence at the next QRS complex When the second QRS complex is between two lines, take the mean of the two numbers from the sequence or use the finetuning method listed below The HR may be counted by simply dividing 300 by the number of the large squares between two heart beats (RR) If the interval between two beats is one large square, the HR is 300 beat/min, 2 squares →150, 3 squares →100, 4 squares → 75, 5 squares → 60, 6 squares → 50 beat/min Figure 1 Calculating heart rate on EKG sheet, HR ~ 1 2



Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog
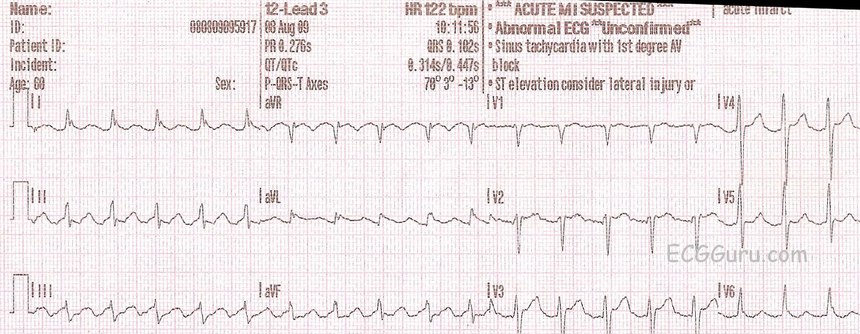
A PAC is a _____ premature beat from the sinus node late beat from the atria An EKG tech is preparing a patient for an exercise stress test Which of the following leads should the tech place on the lower right side of the anterior torso?Interpreting EKG Rhythm Strips Step 1 – Heart Rate Methods to determine heart rate The 6 second method Denotes a 6 second interval on EKG strip Strip is marked by 3 or 6 second tick marks on the top or bottom of the graph paper Count the number of QRS complexes occurring within the 6 second interval,Reading an EKG can be intimidating but the key is forming a system that works for you Step 8 Overall interpretation Rate Quick Estimate "300, 150, 100, 75,
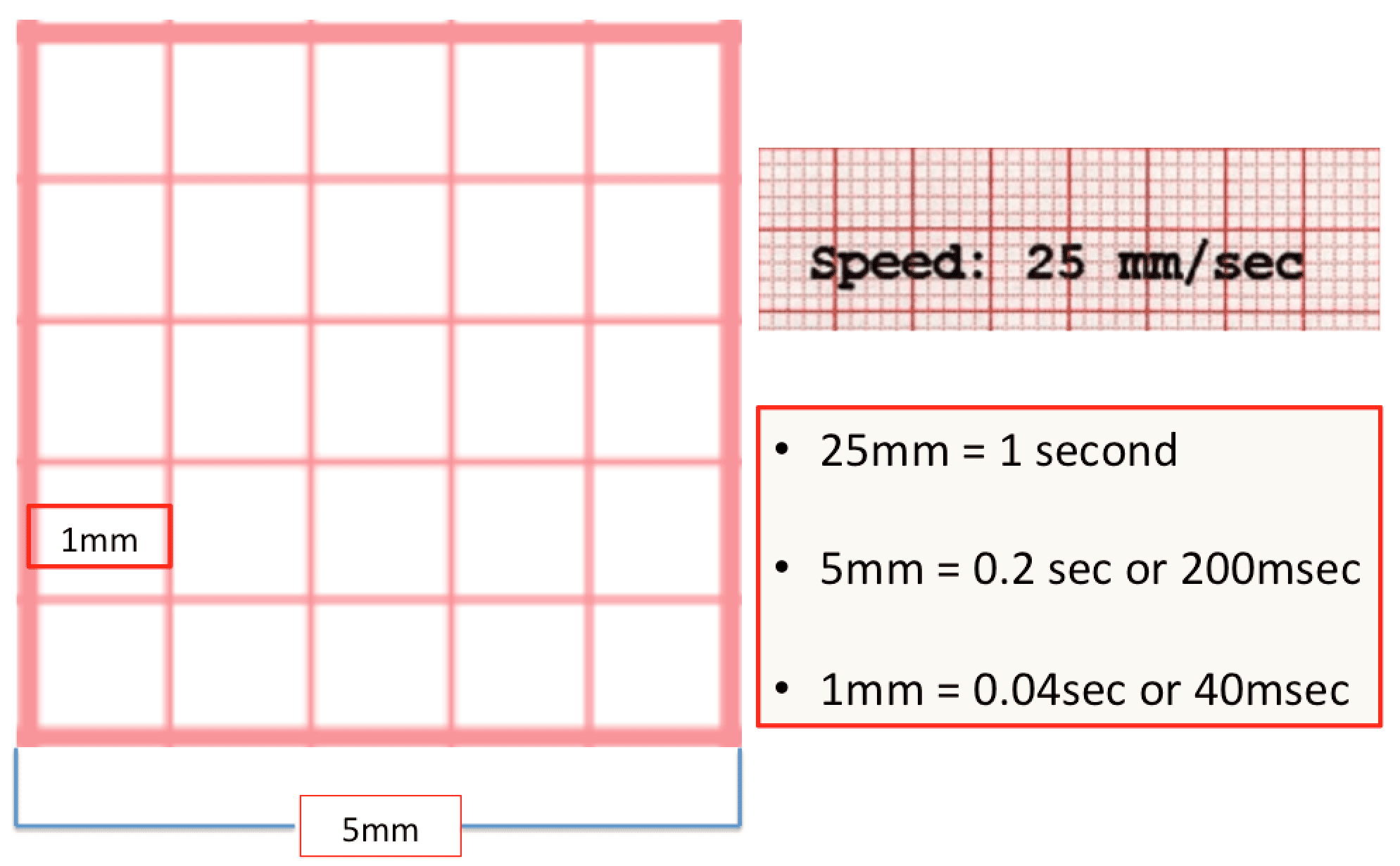
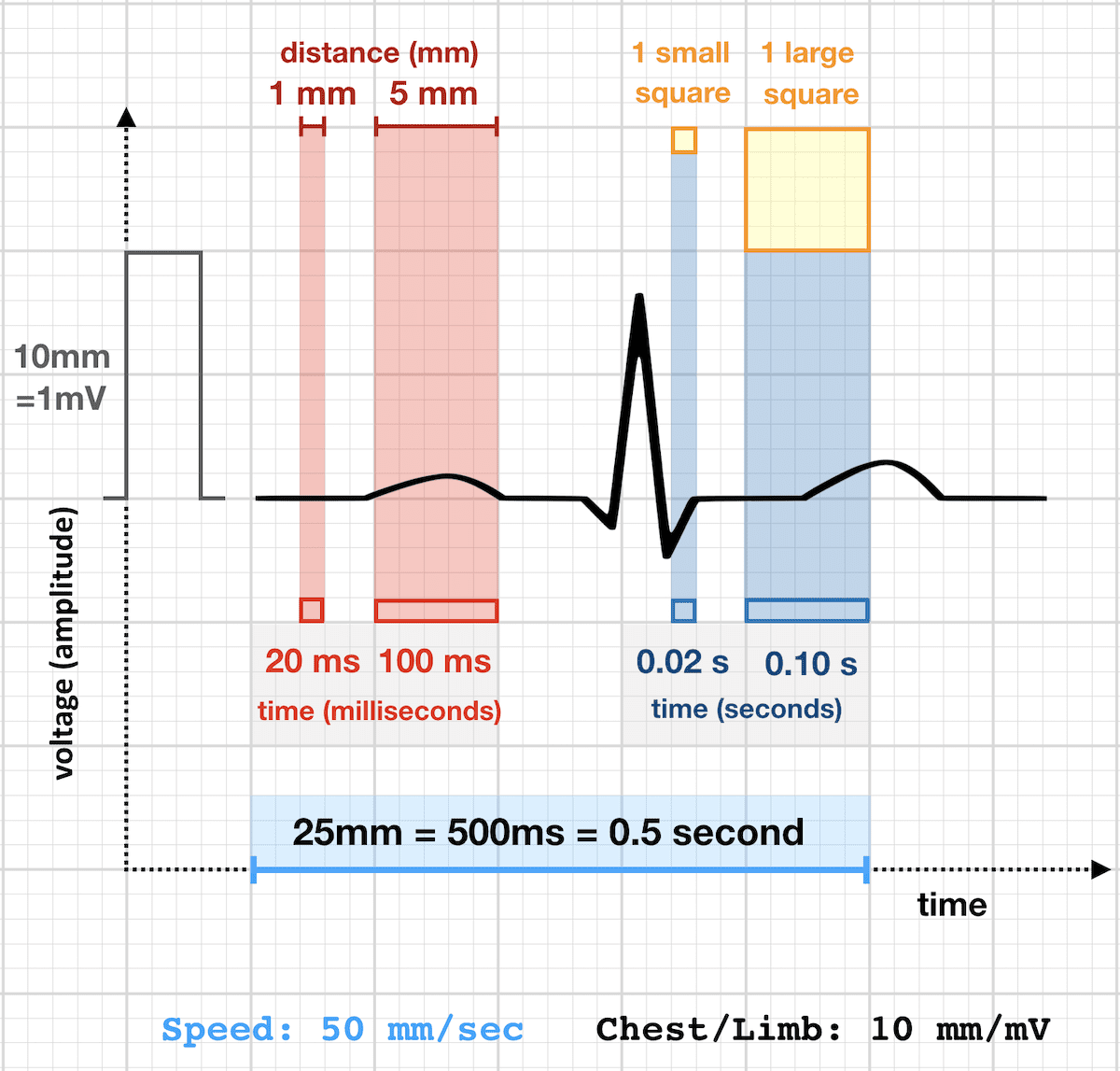
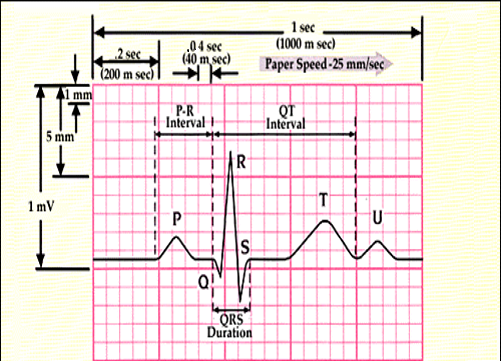
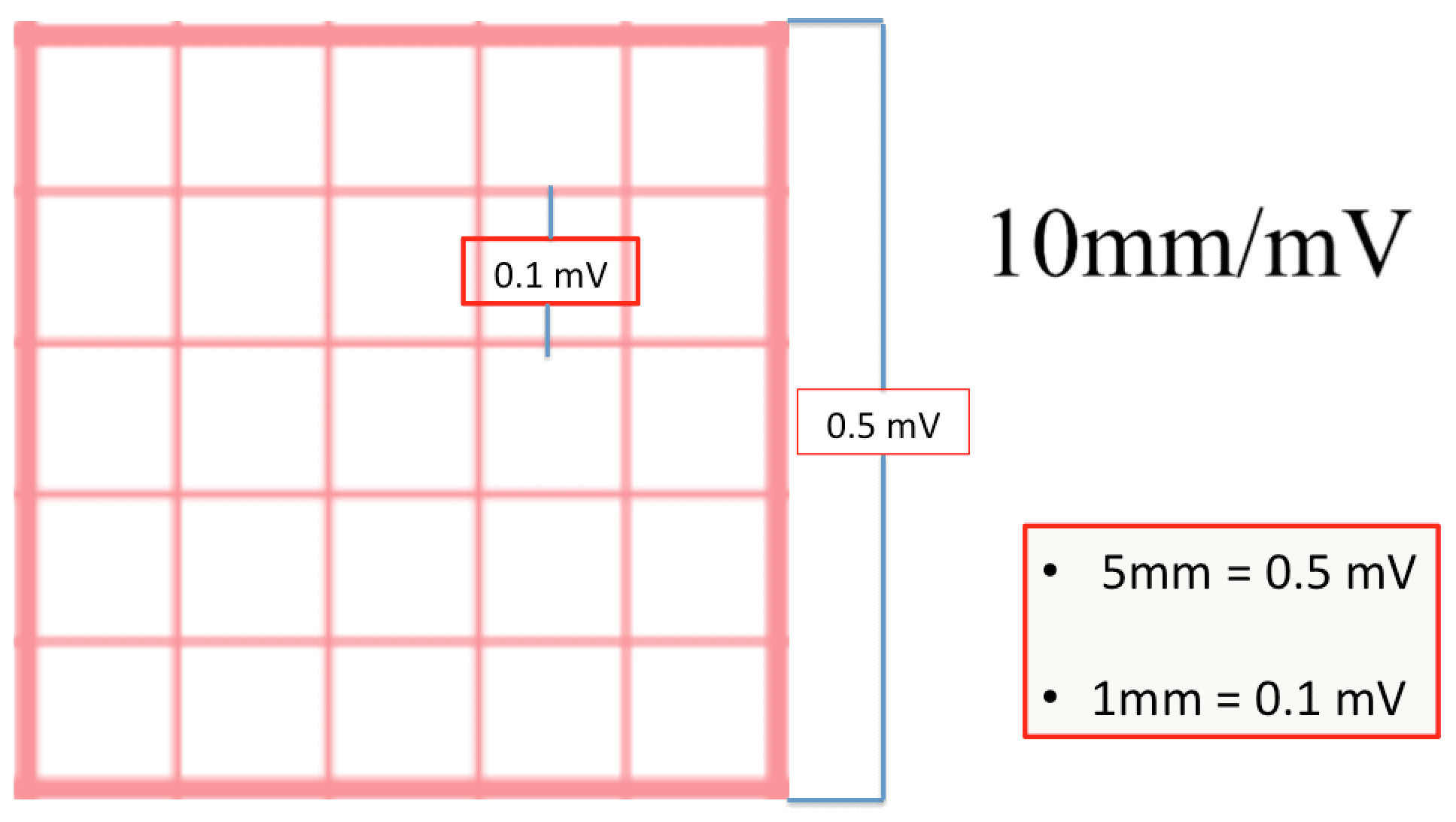
An echocardiogram cost about $300 and the stress test can cost anywhere from $500 to $1,000 These costs do not include any prescribed medications, repeat visits, or hospital stays If your PCP believes that your symptoms warrant a cardiologist visit without insurance, ask for referrals to government and university hospitals;//wwwyoutubecom/channel/UCTaUT2d9ihaeIg6nfmc3TqgMit der Zahlenreihe kannThe vertical, or y axis, on the ECG is voltage, with each millimeter (mm) of paper equal to 01 millivolt (mV) (Fig 11) For practical purposes, we often refer to the amplitude, or height, of an ECG complex in millimeters of paper rather than in millivolts At the beginning or end of the ECG, you may see a square wave, machine induced, that is
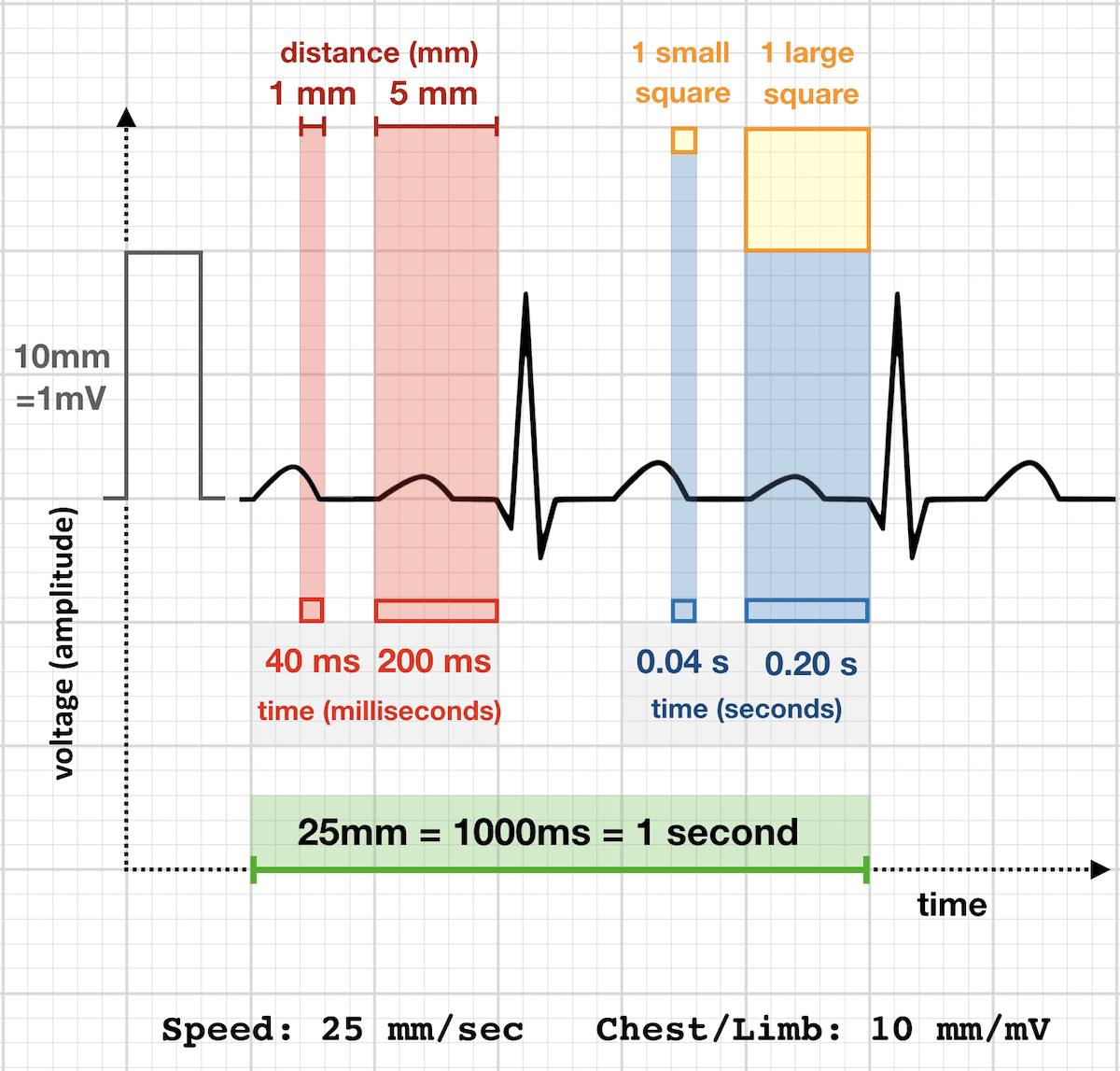
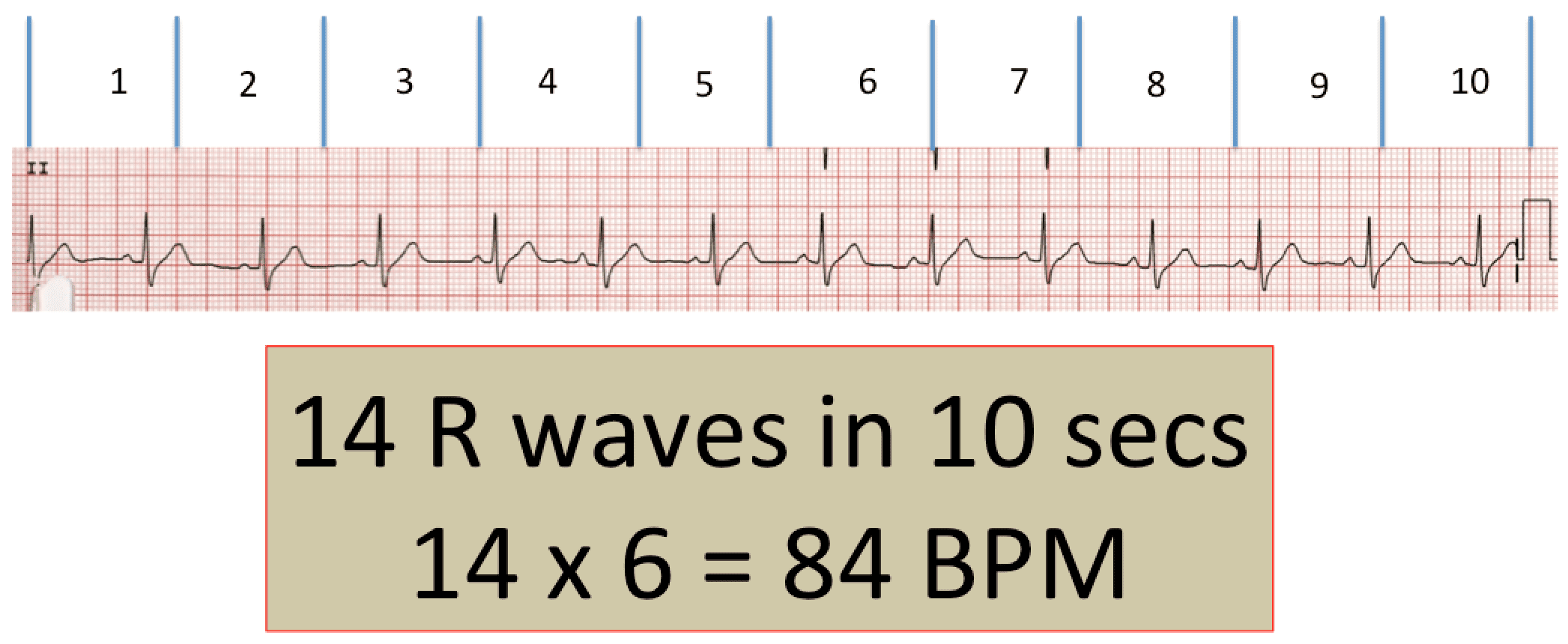
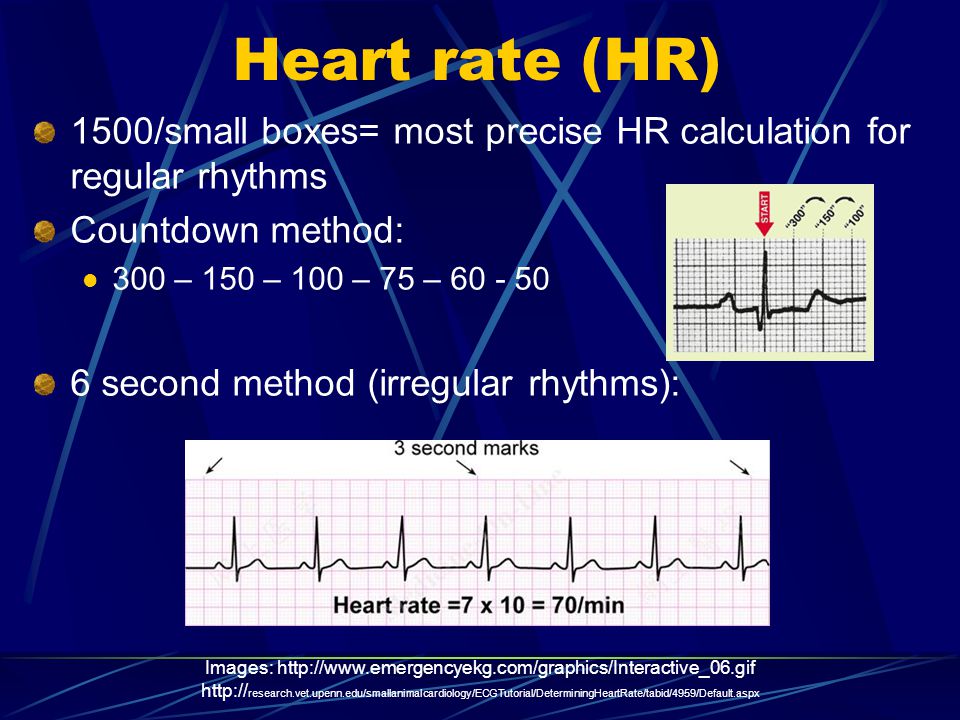
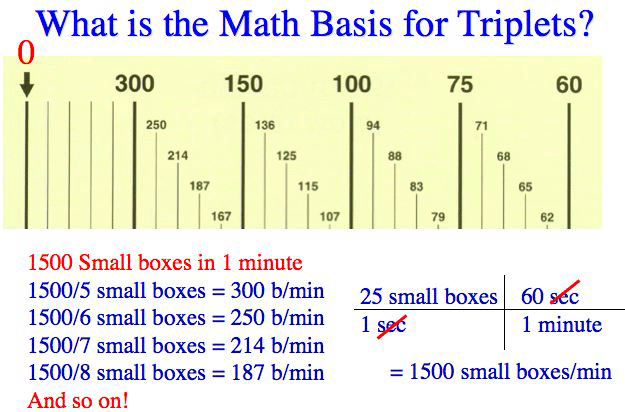
Basic EKG interpretation Heart rate The standard paper speed is 25 mm (5 large squares)/sec This means that if the distance between two beats (RR) is 5 large squares, the HR is 60 beat/min If the distance between two beats is one large square, the HR is 300 beat/min Two squares →150, 3 squares →100, 4 squares → 75, 5 squares → 60 4 Divide the number 300 by your answer above Once you have calculated the number of big squares separating QRS complexes (let's use 32 as an example), perform the following calculation to determine heart rate 300/32 =The EKG Electrodes 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 37, 33, 30 Method # 2 The Six Second Tracing Method Obtain a six second tracing (30 five mm boxes) and count the number of R waves that appear within that 6 second period and multiply by 10 to obtain the HR/min



How To Calculate The Heart Rate On An Ekg



How To Compute The Rate Youtube
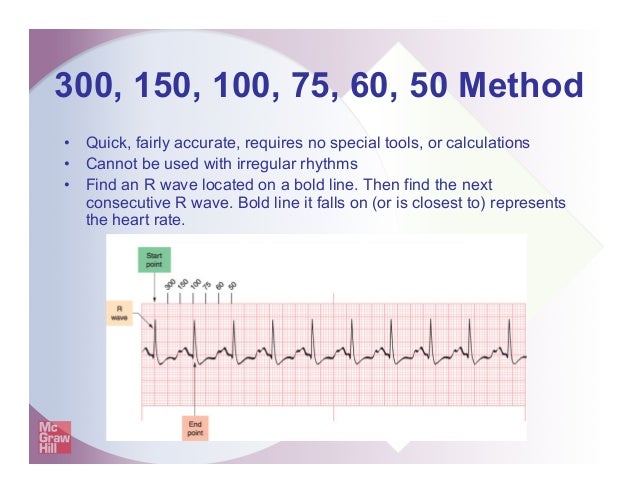
To use the sequence method, find an R wave that lines up with one of the dark vertical lines on the ECG paper If the next R wave appears on the next dark vertical line, it corresponds to heart rate of 300 beats a minute The dark vertical lines correspond to 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, and 50 bpmQRS complexes found in a 6second portion of the ECG tracing • The 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 method involves locating an R wave on a bold line on the ECG paper, then finding the next consecutive R wave and using the 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 values for subsequent bold lines to determine the rateMortara Rangoni Electrocardiograph equipment Chart Paper 108MM X 140MM X 0 Sheets per pack Orig Paper Code , For use with ELI 150 ECG / EKG Machine (5 packs) ZFOLD, Red grid Images are for representational purposes only 5 Packs/Box



1



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley
For example if there is 1 large square between R waves, the heart rate is 300 bpm;Für weitere Videos Schaut auf bitte auf Medi Know!Capture is evidenced on the EKG by the presence of _____ pacemaker spikes at regular intervals paced beats on top of intrinsic beats If a pacemaker fails to fire, what is shown on the EKG



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley




3 Heart Rate Fast Easy Ecgs A Selfpaced
• 300 method – 300, 150, 100, 75, 60 Rate • 10 second method • Each EKG is 10 seconds • Count total QRS complexes • Multiply by 6 Rate • Normal 60 – 100 • Bradycardia < 60 • Tachycardia > 100 Rhythm • Sinus •Atrial • Supraventricular • Junctional • VentricularDivide 300 by the number of large squares obtained in #1 The quotient is the heart rate (cardiac cycles per minute or heart beat per minute) How to determine the heart rate when the rhythm is irregular Method A In a standard EKG tracing, the electrical activity of the heart is measured for 10 continuous seconds12/2/16 3 A Second Look SA Node – bpm Max 150 AV/Junctional Node –4060 bpm Purkinje/Ventricles 40 bpm 13 The Pacing Principle The SA node is the inherent pacemaker of the heart However, the pacemaker that is firing the fastest at



Www Canadianveterinarians Net Documents Dr Meg Sleeper The Abcs Of Ecgs Back To Basics Part I



Ecg Ekg Examples And Quiz Oxford Medical Education
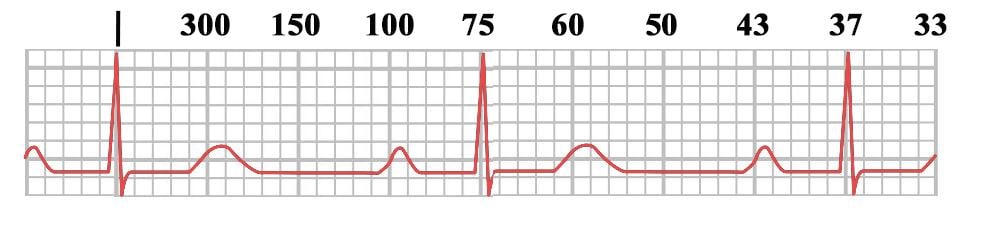
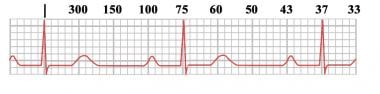
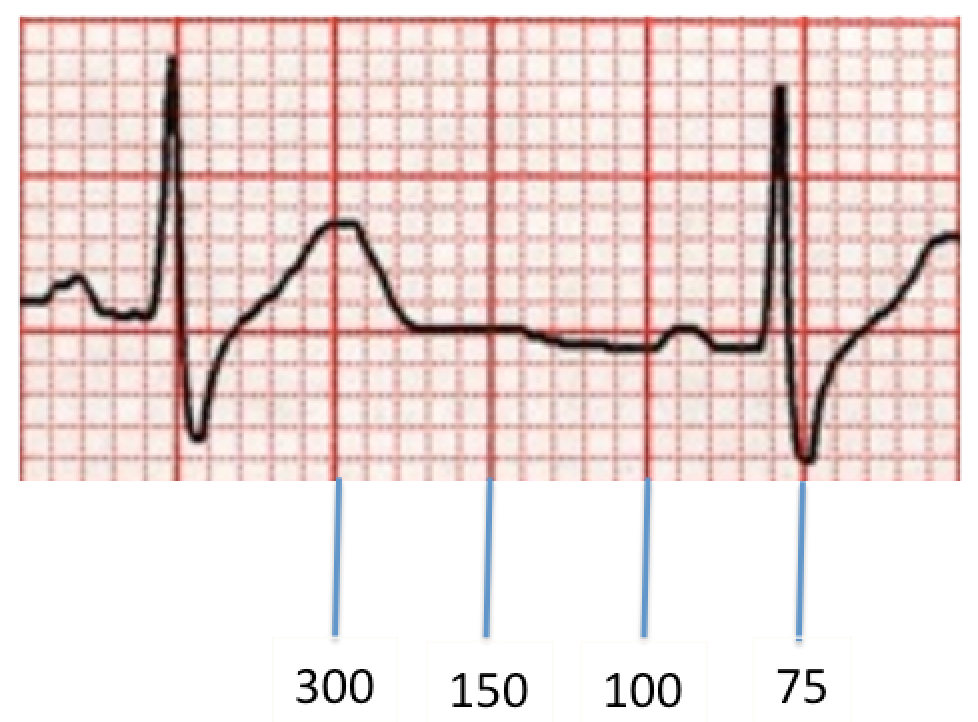
300 150 100 75 60 250 214 187 167 136 125 115 107 94 79 71 68 65 62 START "300" "150" "100 Rapid Interpretation of EKG's by Dale Dubin, MD COVER Publishing Co, PO Box , Fort Myers, FL , USA 1150 9 8 7 6 5 167 1 214 250 300 Components of Normal Sinus Rhythm P Wave The P wave represents depolarization of the right and left atria The EKG Leads The 12lead EKG will be discussed in greater detail later in this course However, at this time we will present an introduction to the EKG leads simply to help explain the basics of Another method, which gives a rough approximation, is the "count off" method Simply count the number of large squares between R waves with the following rates 300 150 100 75 60 For example, if there are three large boxes between R waves, then the rate is 100 beats/min One must extrapolate, however, between boxes



Nursing Bibs Ekg Rate



Clinical Junior Com Ecg Ekg Interpretation Basics How To Read Mi Myocardial Infarction Angina Af Atrial Fibrillation St Elevation Depression
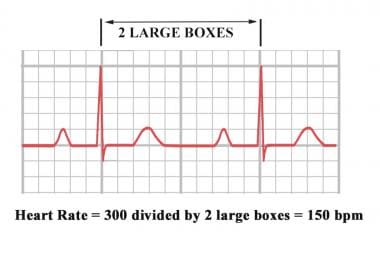
Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the electrical signal from your heart to check for different heart conditions Electrodes are placed on your chest to record your heart's electrical signals, which cause your heart to beat The signals are shown as waves on an attached computer monitor or printer Atrial Flutter on the Electrocardiogram Atrial flutter is distinguishable on the electrocardiogram because it is a rhythmic tachycardia with heart rates that are divisors of 300 bpm, 150 bpm being the most frequent in untreated patients (AV conduction ratio 21) There are no existing P waves, although atrial waves with "sawtooth" pattern are spotted with rates around 300 3 large blocks 100 2 large blocks 150 1 large block 300 We know the "normal" heart rate is (although some would argue that 5090 is more accurate) Using the normal heart rate should have 35 large blocks between Rwaves More than 5 large blocks is a bradycardia and fewer than 3 blocks is a tachycardia



How To Read An Ecg



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley
How to Calculate the Heart Rate on an EKG Education Details On the EKG, locate a R wave that matches a thick line, count the number of large squares to the next R waveHeart rate is 300 divided by the number of large squares, and that's it!View Cheat Sheet CV ECGpdf from PSYC MISC at Texas A&M University RATE 300 150 100 AXIS DEVIATION Normal Left Right 75 60 50 Lead I QRS 43 NORMAL SINUS RHYTHM • There are other ways to calculate heart rate on a 6 second ECG strip, but the rhythm must be regular to do so There is also the 300 method, the 1500 method, and the sequence method Method 2 The 300 Method For the 300 method, you count the number of large boxes between two R waves and divide it by 300



Q Tbn And9gcteww8qp9wt1jydlnb39zitwtewhkghpqdmemgudhgdzr7hks Usqp Cau



Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics
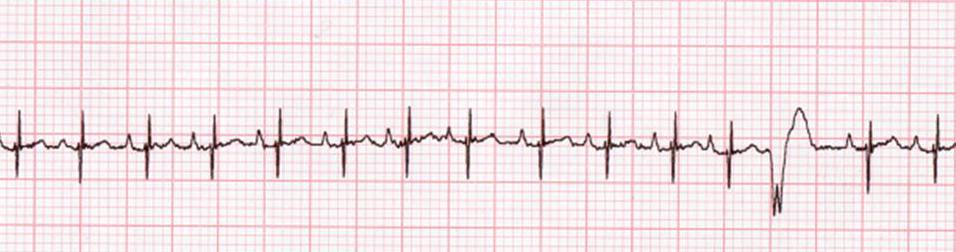
The atrial rate is commonly 300/min, and there is usually a 21 block, resulting in a ventricular response rate of 150/min Other ratios are possible, and sometimes the ratio varies This rhythm is often unstable, and the heart may flip in and out of sinus rhythm, or REGULAR rhythms Rate = 300 / number of LARGE squares between consecutive R waves Very FAST rhythms Rate = 1500 / number of SMALL squares between consecutive R waves SLOW or IRREGULAR rhythms Rate = Number of R waves X 6 The number of complexes (count R waves) on the rhythm strip gives the average rate over a tensecond period This isECG • 12 ldECGlead ECG ECG t i – Complete • ECG strip – Limited information information Rt hth • Rate, rhythm, axis, hth • Rate, rhythm, Ischemia – Easy to get h yper trop h y, ischemia, miscellaneous 300 150 100 75 60 50 43




Ekg Ch 3 Analysis And Interpretation Flashcards Quizlet




12 Lead Ecg Placement Aed Superstore Resource Center
Reading an EKG can be intimidating but the key is forming a system that works for you "300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50The electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) represents the summary of electrical events taking place in the heart Electrodes, adhesive patches placed on the chest and • , each small block = 30 bpm • , each small block = 10 bpm • , each small block = 5 bpmTwo large squares, 150



How To Calculate The Heart Rate On An Ekg



Www Asapa Org Resource Resmgr 17 Spring Frost Ekg Review 5bcompatibil Pdf
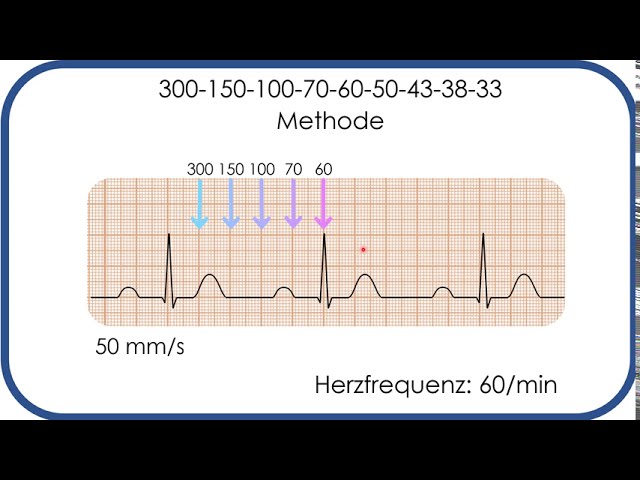
Review some aspects of EKG that are troubling to some in the field 5 Learn from a couple of unique situations What NOT 1 A comprehensive review of all aspects of EKG Box count method large boxes 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 Rate= Normal, 64 P for every QRS, QRS for every P Normal and consistent P's and PR's Normal Sinus Rhythm P P P 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 37, 33 The heart rate irregular rhythm If the heart rate is irregular, count the number of QRS complexes on the ECG and multiply by 6 to obtain the average heart rateRate, rhythm and axis from an ECG 1)Rate The ECG paper runs at 25 mm/sec through the ECG printer Use the sequence Count from the first QRS complex, the first thick line is 300 bpm, the next thick line 150 etc Stop the sequence at the next QRS complex



Http Samples Jbpub Com Ch04 Pass02 Levine Pdf



Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics
Interval between complexes Count large boxes (02 seconds) between complexes;EKG PFS MVR Electronic Inspection Traditional Inspection APS TPF Xpress No automatic exams 0 – 49,999 Cholesterol 300 300 300 300 300 300 Ratio 45 55 60 50 55 60 Cholesterol Treatment 135/80 140/90 150/90 140/85 150/90 155/95 Family History2 No death or occurrence CAD, CVA or Familial CancersDivide 300 by box count 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50




Ecg Basics Methods Of Heart Rate Calculation Youtube Nursing School Notes Nursing School Survival Nursing Notes




Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog
In this video, I demonstrate how to use the Big Box Method (AKA "the 300 method") to determine the heart rate on an ECG Check out the 6 second method tooEKG Practice Drills EKG Reference Guide ECG Graded Quiz EKG Intro Course ECG Tutor ECG Monitor Drill ECG Monitor Quiz 12 Lead ECG ECG 12 Lead Interpretation Tutor Español EKG Lessons Blood Pressure Taking Blood Pressure Basic Procedures Adult Part I Adult Part II Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension Use the heavy boldfaced lines that indicate 3 second increments to count the number of p or rwaves in one minute Memorize the following sequence of numbers as stated in the ECG Strip Ease Book, "300, 150, 100, 75, 60,50 4 " Start with the pwave or rwave (according to which rate you are measuring) closest to a heavy line on the EKG paper




Determining Rate Learn The Heart



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley
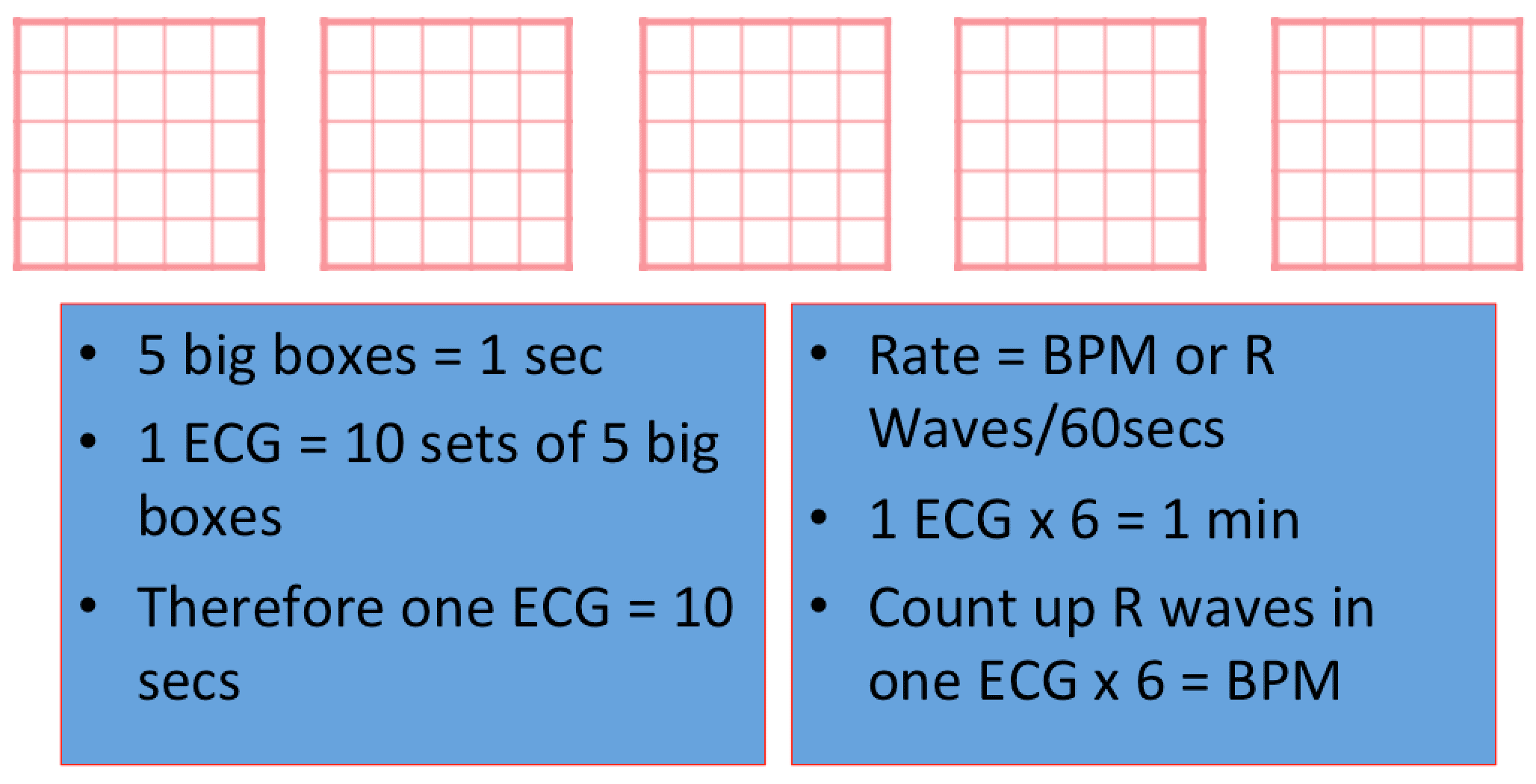
Heart rates associated with each of the large boxes in the following order are 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50, 43, 37, 33 beats per minute (bpm) Heart rate boxes ST depression 2 The Six Second Method Get 6 seconds of ECG tracing (ie 30 big boxes) and count the number of R waves that appear within that 6 second period and multiply by 10 Another version of this is the 10 second method (ie 50 big boxes) and count the number of R waves that appear within that 10 second period and multiply by 6 This is a great method for slow or irregular Distance markers on EKG represent 15 large boxes (3 seconds) Count QRS Complexes between spanning 2 distance markers (30 large boxes, 6 seconds) Multiply complex count by 10 for Heart Rate per minute;




Dubin S Rapid Interpretation Of Ekg Flashcards Quizlet



Ecg For Interns Online Presentation
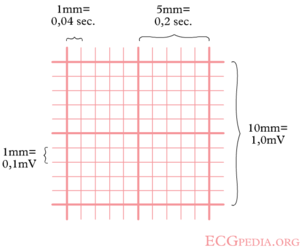
Using the method 300 150 100 75 60 in the above example, 3 large boxes noted between two Rwaves, followed by roughly 25 small boxes would represent a ventricular rate of 85/min Another method is to divide 1500 by the number of small squares between two RwavesAdvanced Nurse Aide $3050 Down payment $270 (due at time of registration, $100 for registration & $170 for books) 8 weekly payments of $0 7 weekly payments of $150 1 weekly final payment of $130 Fast Track Program Down payment of $1,525 and 7 weekly payments of $195 and a final payment of $160The ECG has a grid with thick lines 5 mm apart (= 0, second) and thin lines 1 mm (0,04 second) There are three simple methods to determine the heart rate (HR) The square counting method The square counting method is ideal for regular heart rates Use the sequence




Sinus Tachycardia Wikipedia



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley



Www fp Org Dam fp Documents Events Nc Handouts Nc17 Ekg Pdf




Ekg Interpretation
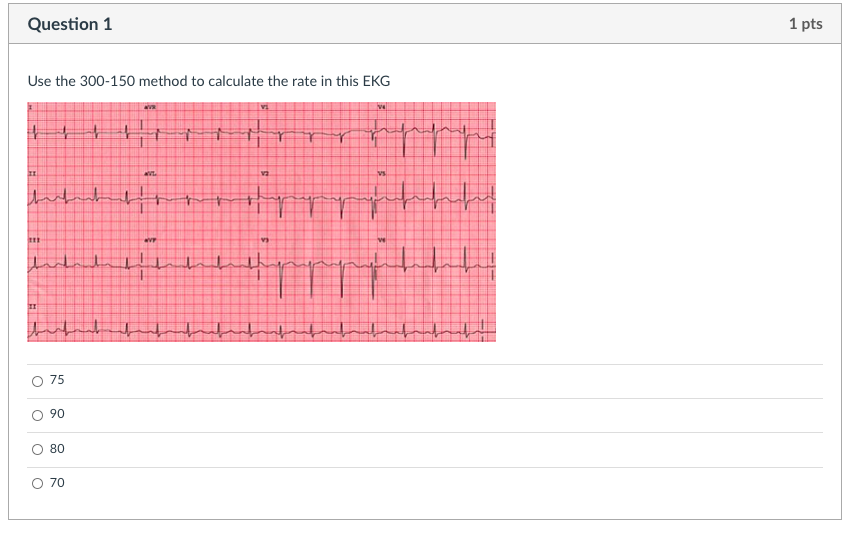



Question 1 1 Pts Use The 300 150 Method To Calculate Chegg Com



Ecg A Pictorial Primer
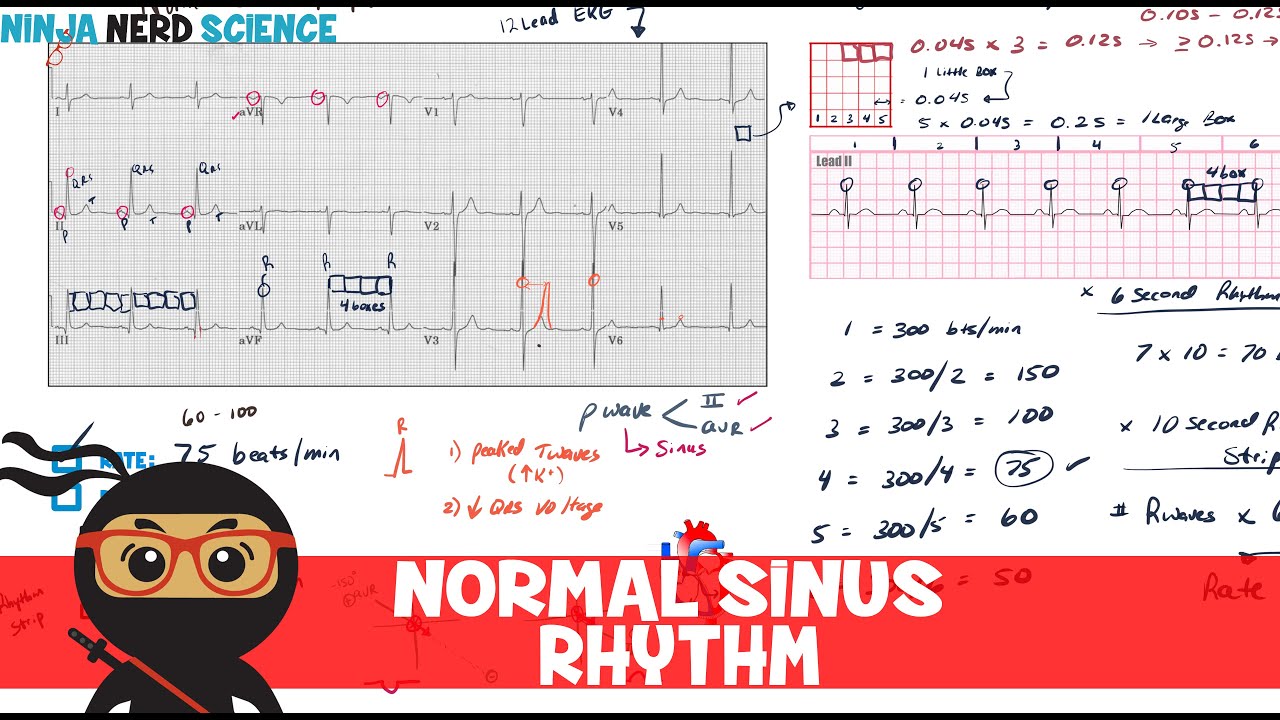



Rate And Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Youtube




Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics




Ekg Interpretation Cheat Sheet 1 Rate Regular Grepmed



1



Ecg A Pictorial Primer



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley




How To Calculate Heart Rate From Ecg Arxiusarquitectura




How To Read An Ecg Wikidoc




Rate
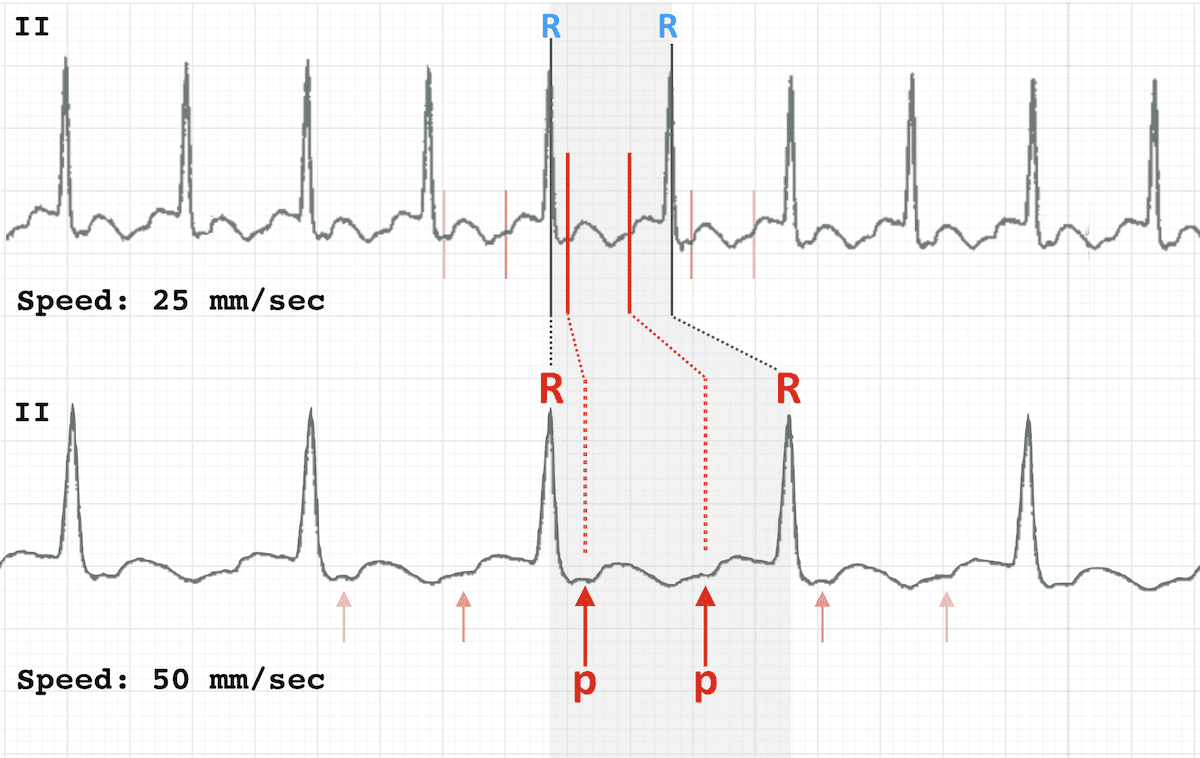



Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics




Pediatric Ekg Interpretation



Large Block Method To Calculate Heart Rate Ecg Medical Training



Nursing Bibs Ekg Rate



Basic Arrhythmias C 11 American Heart Association Do Not Edit Ppt Download



How To Read An Ecg



How Is The Heart Rate Determined On Electrocardiography Ecg




Ecg



Ekg Paper Ems Education



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley




Calculation Of Heart Rate Rhythm Basis On Ecg Recording Youtube




Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics



How Is The Heart Rate Determined On Electrocardiography Ecg



How To Read An Ecg Physical Therapy Reviewer
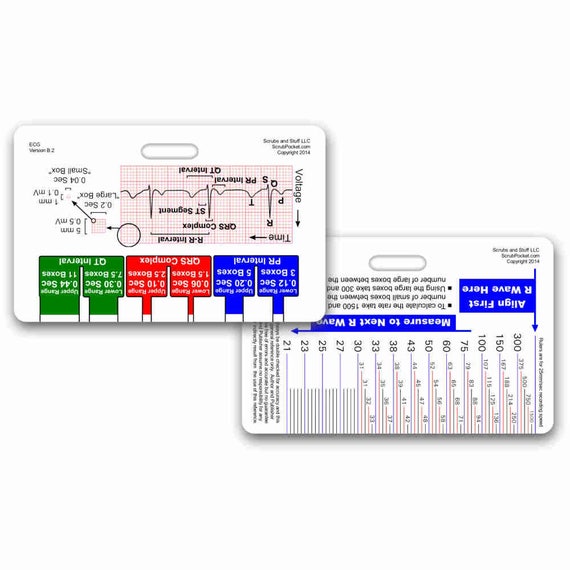



Ekg Ruler Badge Pocket Card Horizontal For Nurse Paramedic Emt Etsy



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley




How To Find Heart Rate Pulse From Ekg Youtube



Ecg A Pictorial Primer




The Second Method Uses Small Boxes Count The Number Grepmed



Http Www Bremss Org Uploadedfiles File Ekg Intermediate Tips Tricks Tools Pdf



The Whole Ecg A Really Basic Ecg Primer



Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog



Reading Ecgs In Veterinary Patients An Introduction




Ekg Interpretation Em In 5



Ekg Module 2



Large Block Method To Calculate Heart Rate Ecg Medical Training



Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog



Ekg Befundung Herzfrequenz In Sekunden Bestimmen 300 150 100 Methode Youtube



10 Tips To Diagnose Atrial Flutter On An Ekg




My Notes For Usmle Basics For The Wards How To Read Ekgs




Cv Physiology Determining Heart Rate From The Electrocardiogram



3



Rate Ecgpedia



Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog




Medicowesome Mnemonics And Basics Of Ecg Interpretation




The Beat Goes On The Mind Can Only Learn What The Butt Can Endure Ppt Download



Rate Ecgpedia



Ekg Interpretation Ppt Video Online Download




Ekg Atrial Flutter Rush Emergency Medicine



Cardiac Cycles



Ecg Basics Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog
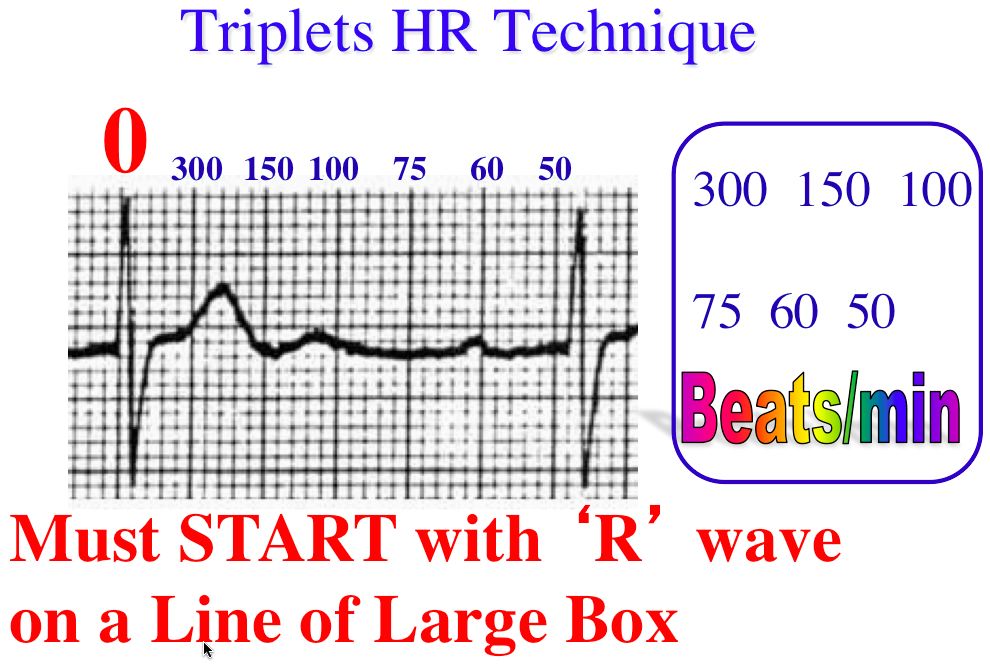



Triplets R To R 6 Second Heart Rate Method



The Whole Ecg A Really Basic Ecg Primer
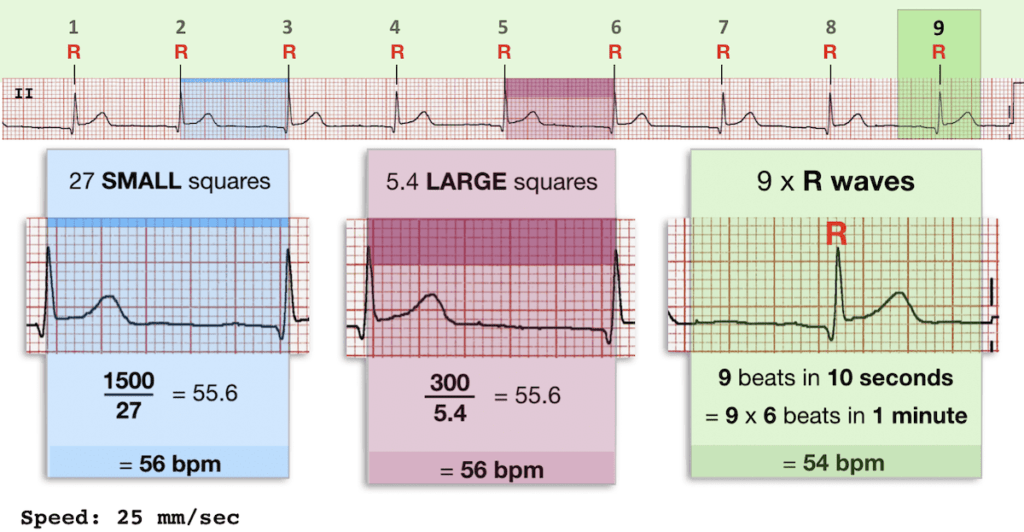



Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics
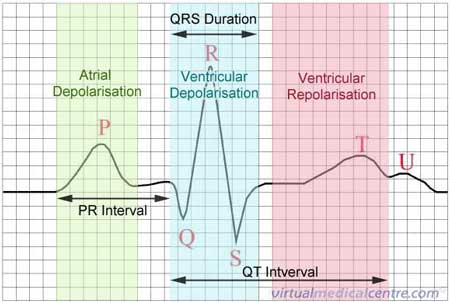



How To Read An Ecg




Ecg Interpretation Ppt Download
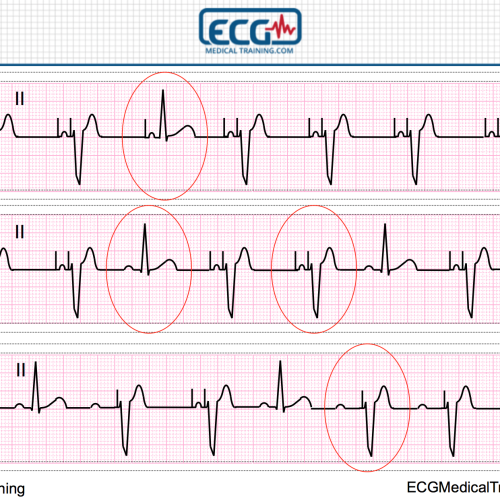



Large Block Method To Calculate Heart Rate Ecg Medical Training




Heart Rate The Premier Ekg Resource For Medical Professionals Ekg Md Dr Anthony Kashou
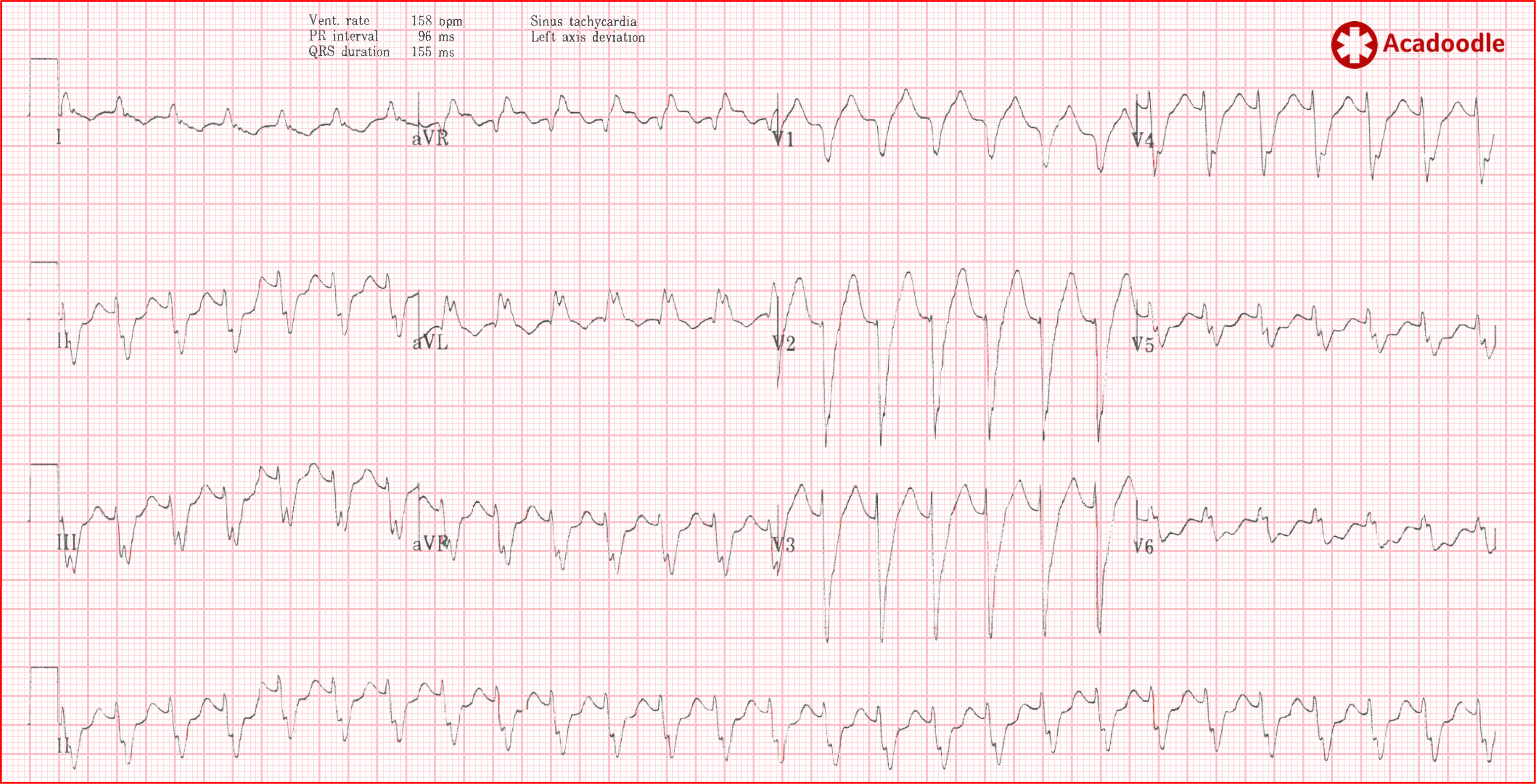



Why Does Atrial Flutter Fool Us So Often Top 10 Tips To Minimize Uncertainty Learn Advanced



Large Block Method To Calculate Heart Rate Ecg Medical Training



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley
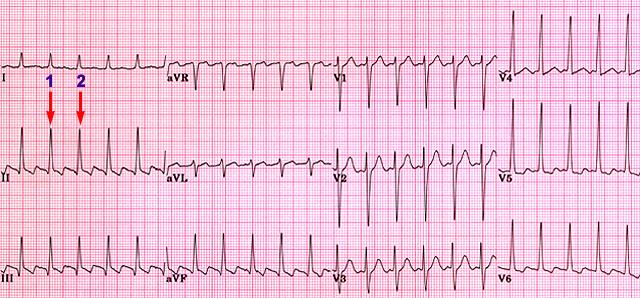



Step 1 Determine The Heart Rate




Using The 300 150 100 75 60 50 Method Youtube




Cardiac Conduction Identifying Rhythms Ppt Download




Ekg Interpretation



Triplets R To R 6 Second Heart Rate Method



Ecg Rate Interpretation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics



Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View 636 Heart Rate Fast And Easy Ecgs Shade Wesley



Shadechapter03 Ppt Read Only




Ecg Basics Methods Of Heart Rate Calculation Youtube




Determine Hr From A Regular Rhythm Ekg 1500 300 Methods Youtube



The Whole Ecg A Really Basic Ecg Primer



Large Block Method To Calculate Heart Rate Ecg Medical Training



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿